Email phishing scams are used to steal confidential information from users – most often login credentials and credit card numbers – through malicious email links. These scammers trick their victims by pretending to be a legitimate, trusted source. Then the recipient opens the email and clicks the malicious link. This link often installs malware that locks users out of their information unless a ransom is paid. If credit card information is obtained fraudulent purchases can be made or even lead to identity theft.
Phishing attacks aren’t limited to individuals, corporations are extremely vulnerable to these attacks as well. It just takes one employee to accidentally click the link within the malicious email and expose their company to threats across their network. Attacks like this can lead to severe financial loss and even leaks of private company or customer data.
Phishing scams are most often through email, but with the rise of social media, it is now common for these to be on social media, messaging apps, and other popular platforms. So it’s important to understand how to spot phishing attempts.
Would you fall for a phishing email? Take our test here to find out!
How to Spot a Phishing Attempt:
Phishing emails are some of the easiest attacks for cybercriminals to conduct and are dangerously on the rise. Primarily a numbers game, they mass email out these scams, hoping for at least a couple of bites. And statistics are unfortunately on their side.
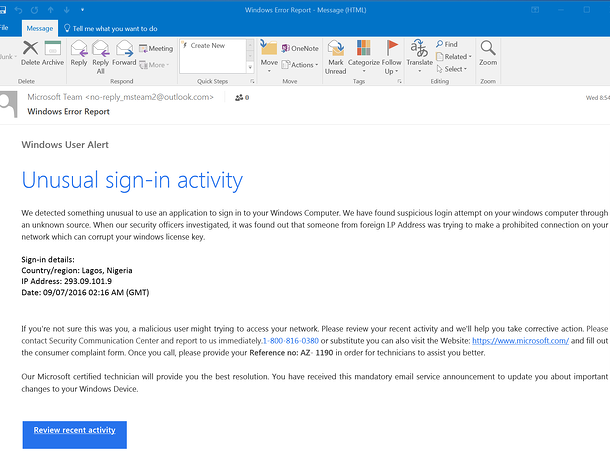
Due to the nature of phishing attacks, it’s easy to fall for one at first glance. The source looks legitimate, the content appears urgent and important – but on further inspection, you can start to piece together their flaws. We’ve included a few examples to look out for so you don’t get caught in a scam:
Design – Phishing emails are designed to look as legitimate as possible. Clean emails with appropriate phrasing, logos, fonts, etc. all work to make it look like it’s from the proper source.
Sense of Urgency with Push for Action – Keep an eye out for emails with threats to shut off service, close your account, hacked account warnings, etc.
Poor grammar or spelling – While scammers do their best to phrase these emails in perfect English, many fall short. Spelling and grammar errors are common in phishing emails and highly unlikely when from a legitimate source.
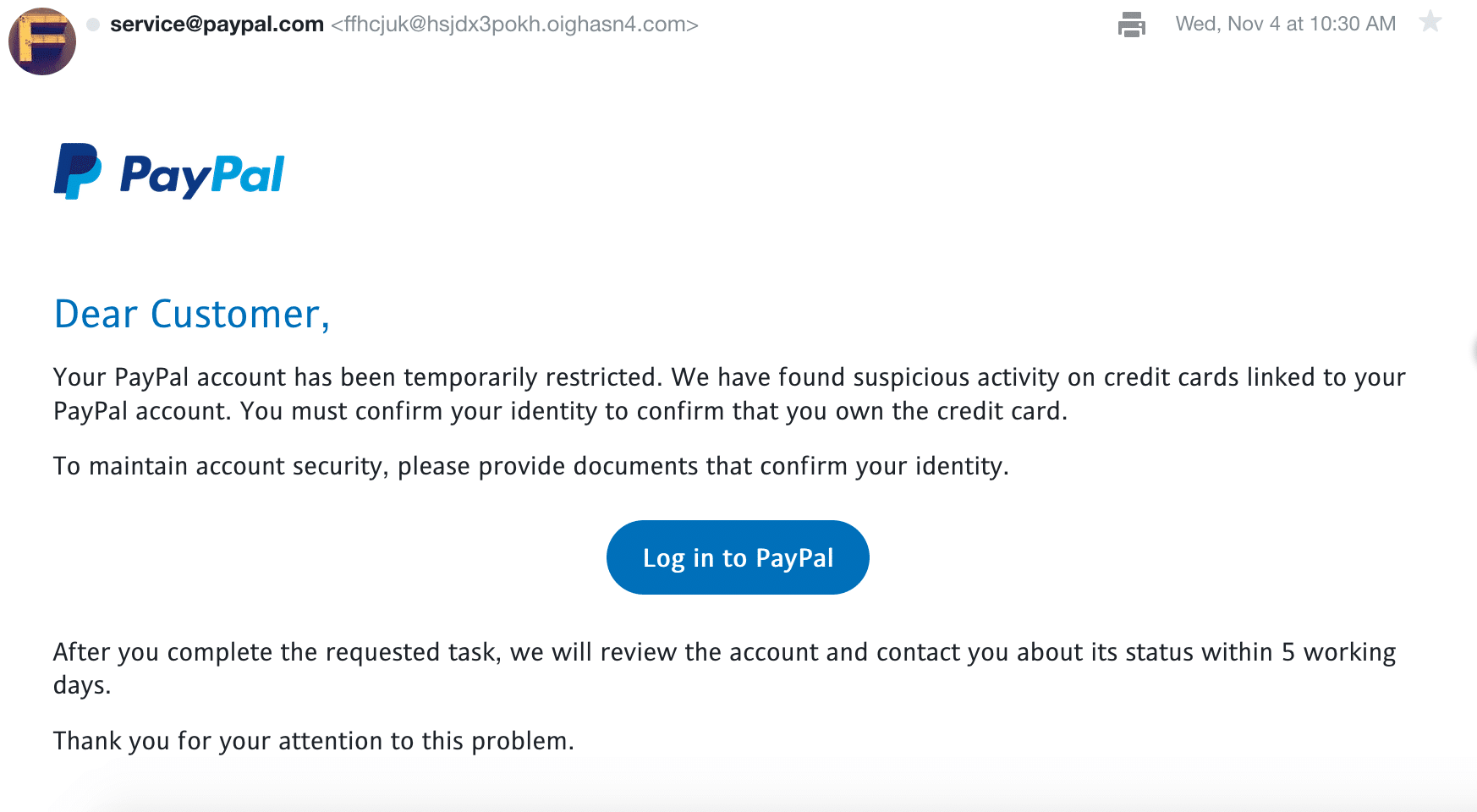
Strange Sent From Emails – You may notice emails come from a long string of numbers at letters at a domain that is not the actual company. In the PayPal example below you’ll see it looks like it is coming from service@paypal.com but on closer inspection -> ffhcjuk@hsjdx3pokh.oighasn4.com (definitely not PayPal).
Hover the Links: When you hover over the links you may see a small preview at the bottom of your browser or on your mouse tip. This link is often a very clear indicator of the scam. The example below attempted to use LinkedIn shared pages to redirect you to a malicious website. A popular tactic. Why would PayPal ever use a LinkedIn link? That’s reason enough not to click. But remember – NEVER click the links.
Preventing Phishing Emails:
The best way to prevent phishing emails is through human knowledge. Testing yourself or employees on phishing simulations and understanding the common indicators an email is a scam are the best ways to protect your business. In one example, a phishing attack was shut down across an entire organization in just 19 minutes because the employees had been trained and identified the scam and quickly notified IT support to resolve.
How can QSG Help?
Take advantage of our phishing simulation to put your employees and coworkers to the test. Our phishing tests help increase employee awareness of these attacks by 25% and educate your employees on how to spot and avoid them when they do strike. Contact Us to schedule your phishing simulation.